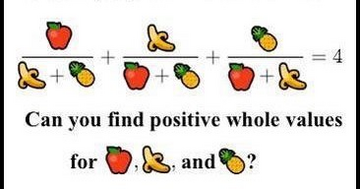AMS Student Chapter Seminar: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→February 22, Wil Cocke: title and abstract) |
No edit summary |
||
| (271 intermediate revisions by 29 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The AMS Student Chapter Seminar is an informal, graduate student | The AMS Student Chapter Seminar (aka Donut Seminar) is an informal, graduate student seminar on a wide range of mathematical topics. The goal of the seminar is to promote community building and give graduate students an opportunity to communicate fun, accessible math to their peers in a stress-free (but not sugar-free) environment. Pastries (usually donuts) will be provided. | ||
* '''When:''' | * '''When:''' Thursdays 4:00-4:30pm | ||
* '''Where:''' Van Vleck, 9th floor lounge (unless otherwise announced) | * '''Where:''' Van Vleck, 9th floor lounge (unless otherwise announced) | ||
* '''Organizers:''' | * '''Organizers:''' Ivan Aidun, Kaiyi Huang, Ethan Schondorf | ||
Everyone is welcome to give a talk. To sign up, please contact one of the organizers with a title and abstract. Talks are | Everyone is welcome to give a talk. To sign up, please contact one of the organizers with a title and abstract. Talks are 25 minutes long and should avoid assuming significant mathematical background beyond first-year graduate courses. | ||
The schedule of talks from past semesters can be found [[AMS Student Chapter Seminar, previous semesters|here]]. | The schedule of talks from past semesters can be found [[AMS Student Chapter Seminar, previous semesters|here]]. | ||
== | == Fall 2024 == | ||
<center> | |||
{| cellspacing="5" cellpadding="14" border="0" style="color:black; font-size:120%" | |||
! align="center" width="200" bgcolor="#D0D0D0" |'''Date''' | |||
! align="center" width="200" bgcolor="#A6B658" |'''Speaker''' | |||
! align="center" width="300" bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |'''Title''' | |||
! align="center" width="400" bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |'''Abstract''' | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="#D0D0D0" |September 12 | |||
| bgcolor="#A6B658" |Ari Davidovsky | |||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |95% of people can't solve this! | |||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" | [[File:Image.png|360px]] | |||
=== | We will attempt to answer this question and along the way explore how algebra and geometry work together to solve problems in number theory. | ||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="#D0D0D0" |September 19 | |||
| bgcolor="#A6B658" |CANCELLED | |||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |NONE | |||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |NONE | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="#D0D0D0" |September 26 | |||
| bgcolor="#A6B658" |Mateo Morales | |||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |Officially petitioning the department to acquire a ping pong table. | |||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |Ever want to prove something is a free group of rank 2? Me too. One way to do this is to use a ping pong argument of how a group generated by two elements acts on a set. | |||
I will illustrate the ping pong argument using an example of matrices, explain how it works, and explain why, kinda. | |||
Very approachable if you know what a group is but does require tons of ping pong experience. | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="#D0D0D0" |October 3 | |||
| bgcolor="#A6B658" |Karthik Ravishankar | |||
=== | | bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |Incompleteness for the working mathematician | ||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |In this talk we'll take a look at Gödels famous incompleteness theorems and look at some of its immediate as well as interesting consequences. No background in logic is necessary! | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="#D0D0D0" |October 10 | |||
| bgcolor="#A6B658" |Elizabeth Hankins | |||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |Mathematical Origami and Flat-Foldability | |||
= | | bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |If you've ever unfolded a piece of origami, you might have noticed complicated symmetries in the pattern of creases left behind. What patterns of lines can and cannot be folded into origami? And why is it sometimes hard to determine? | ||
|- | |||
=== | | bgcolor="#D0D0D0" |October 17 | ||
| bgcolor="#A6B658" |CANCELLED | |||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |NONE | |||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |NONE | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="#D0D0D0" |October 24 | |||
=== | | bgcolor="#A6B658" |CANCELLED | ||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |NONE | |||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |NONE | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="#D0D0D0" |October 31 | |||
| bgcolor="#A6B658" |Jacob Wood | |||
=== | | bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |What is the length of a <s>potato</s> pumpkin? | ||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |How many is a jack-o-lantern? What is the length of a pumpkin? These questions sound like nonsense, but they have perfectly reasonable interpretations with perfectly reasonable answers. On our journey through the haunted house with two rooms, we will encounter some scary characters like differential topology and measure theory. Do not fear; little to no experience in either subject is required. | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="#D0D0D0" |November 7 | |||
| bgcolor="#A6B658" |CANCELLED: DISTINGUISHED LECTURE | |||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |NONE | |||
== | | bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |NONE | ||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="#D0D0D0" |November 14 | |||
| bgcolor="#A6B658" |Sapir Ben-Shahar | |||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |Hexaflexagons | |||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |Come along for some hexaflexafun and discover the mysterious properties of hexaflexagons, the bestagons! Learn how to make and navigate through the folds of your very own paper hexaflexagon. No prior knowledge of hexagons (or hexaflexagons) is assumed. | |||
= | |- | ||
| bgcolor="#D0D0D0" |November 21 | |||
= | | bgcolor="#A6B658" |Andrew Krenz | ||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |All concepts are database queries | |||
= | | bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |A celebrated result of applied category theory states that the category of small categories is equivalent to the category of database schemas. Therefore, every theorem about small categories can be interpreted as a theorem about databases. Maybe you've heard someone repeat Mac Lane's famous slogan "all concepts are Kan extensions." In this talk, I'll give a high-level overview of/introduction to categorical database theory (developed by David Spivak) wherein Kan extensions play the role of regular every day database queries. No familiarity with categories or databases will be assumed. | ||
|- | |||
= | | bgcolor="#D0D0D0" |November 28 | ||
| bgcolor="#A6B658" |THANKSGIVING | |||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |NONE | |||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |NONE | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="#D0D0D0" |December 5 | |||
| bgcolor="#A6B658" |Caroline Nunn | |||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |Watch Caroline eat a donut: an introduction to Morse theory | |||
| bgcolor="#BCD2EE" |Morse theory has been described as "one of the deepest applications of differential geometry to topology." However, the concepts involved in Morse theory are so simple that you can learn them just by watching me eat a donut (and subsequently watching me give a 20 minute talk explaining Morse theory.) No background is needed beyond calc 3 and a passing familiarity with donuts. | |||
|} | |||
</center> | |||
Latest revision as of 19:14, 2 December 2024
The AMS Student Chapter Seminar (aka Donut Seminar) is an informal, graduate student seminar on a wide range of mathematical topics. The goal of the seminar is to promote community building and give graduate students an opportunity to communicate fun, accessible math to their peers in a stress-free (but not sugar-free) environment. Pastries (usually donuts) will be provided.
- When: Thursdays 4:00-4:30pm
- Where: Van Vleck, 9th floor lounge (unless otherwise announced)
- Organizers: Ivan Aidun, Kaiyi Huang, Ethan Schondorf
Everyone is welcome to give a talk. To sign up, please contact one of the organizers with a title and abstract. Talks are 25 minutes long and should avoid assuming significant mathematical background beyond first-year graduate courses.
The schedule of talks from past semesters can be found here.